Using PM2 with AWS Elastic Beanstalk
This page will guide you step by step through the PM2 integration in an AWS Elastic Beanstalk environment.
We will use Git and the Elastic Beanstalk CLI.
Prepare your app
Set your ecosystem file
Generate an ecosystem.config.js template with:
pm2 init
Change the template to suit your needs:
module.exports = {
apps : [{
name: "app",
script: "./app.js",
env: {
NODE_ENV: "development",
},
env_production: {
NODE_ENV: "production",
}
}]
}
Learn more about ecosystem file here.
Add PM2 as a module
Add pm2 as a dependency to your projet.
With npm:
npm install --save pm2
With yarn:
yarn add pm2
Set your package.json
In your package.json, modify the start script to:
{
"scripts": {
"start": "pm2-runtime start ecosystem.config.js --env production"
}
Deploy with Elastic Beanstalk CLI
Create an account on AWS and get your access keys
Sign up for an account on AWS here.
In order to get access keys, you must create an IAM user. You can do that here.
Add a user:
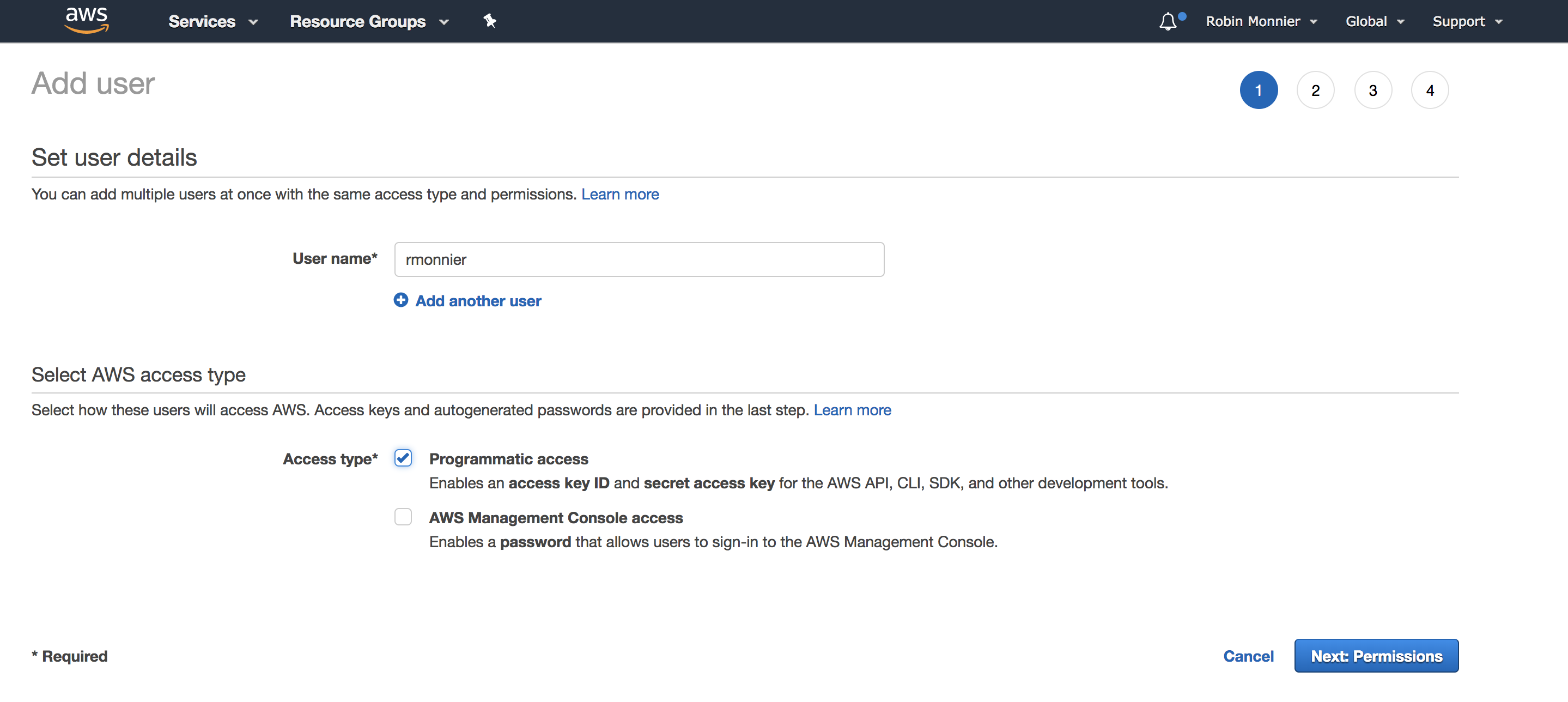
Give it the programmatic access:
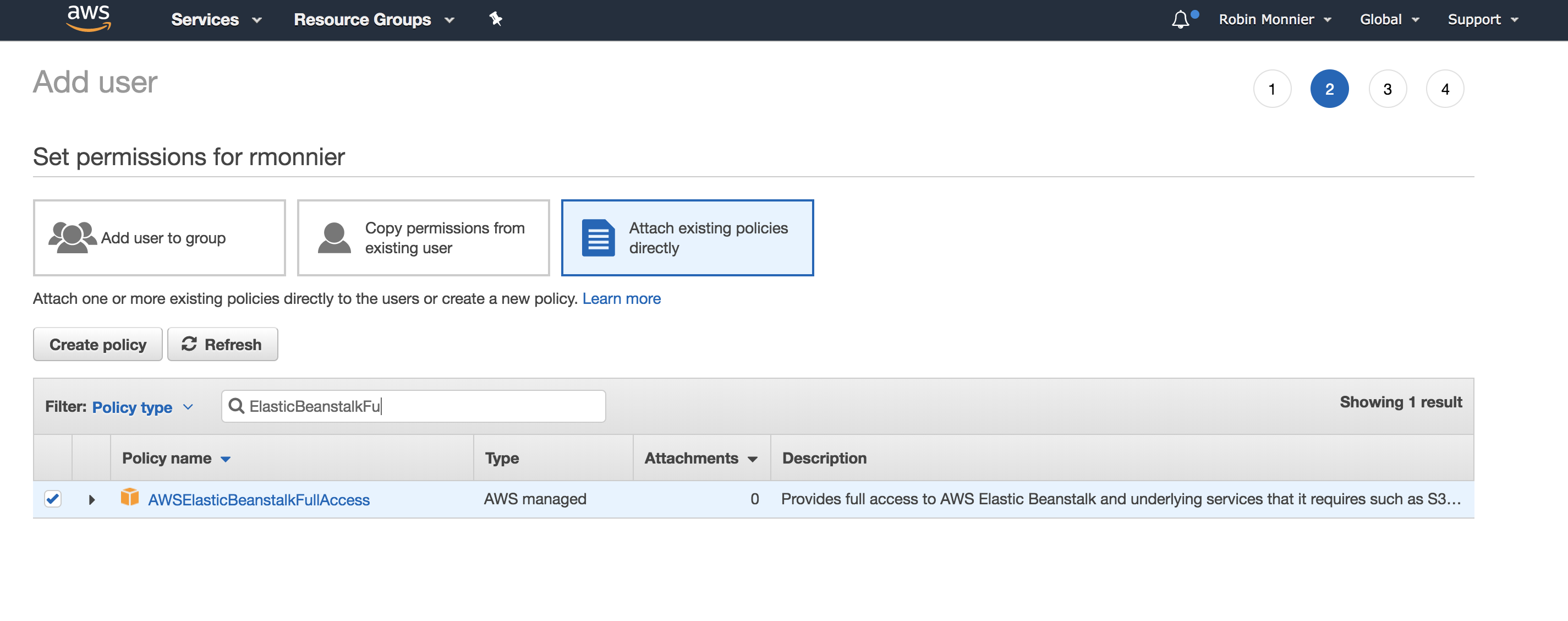
Select the ElasticBeanstalkFullAccess strategy:
Create the user and you will get your access keys:
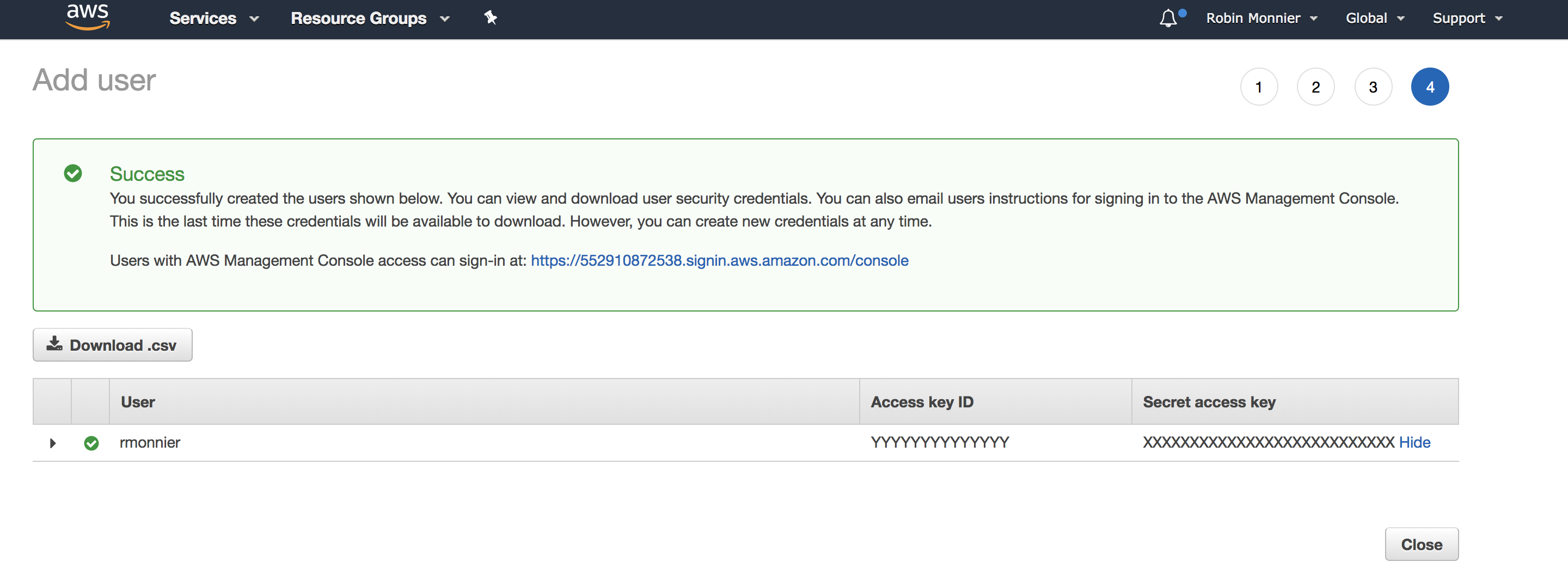
Copy and paste your access-id and your secret-key in your AWS config file (~/.aws/config):
[profile eb-cli]
aws_access_key_id = YYYYYYYYYYYYY
aws_secret_access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Install the CLI
The CLI is available with pip, the python package manager:
pip3 install --upgrade --user awsebcli
Further instructions to install here.
Init your Elastic Beanstalk app
Run eb init -p Node.js to initialize your Node.js app:
eb init --profile eb-cli -p Node.js
Select a default region
2) us-west-1 : US West (N. California)
Select an application to use
[ Create new Application ]
Enter Application Name
eb-pm2-example
Application eb-pm2-example has been created.
Do you want to set up SSH for your instances?
(y/n): n
For a description of each option see the AWS example here
Create an Elastic Beanstalk environment
Each application can have many environments, which is useful to manage separate environments for development, testing or production.
Before creating an environment, make sure to commit your changes. The Elastic Beanstalk uses git archive to create a .zip file from the contents of the most recent git commit command.
To create a new environment, run the following:
eb create eb-pm2-example-env
List all available environments with:
eb list
eb-pm2-example-env
Get environment infos and status with:
eb status
Environment details for: eb-pm2-example-env
Application name: eb-pm2-example
Region: us-west-2
Deployed Version: app-4408-180305
Environment ID: e-gekedaw
Platform: arn:aws:elasticbeanstalk:us-west-1::platform/Node.js running on 64bit Amazon Linux/4.4.5
Tier: WebServer-Standard-1.0
CNAME: eb-pm2-example.us-west-2.elasticbeanstalk.com
Updated: 2018-02-19 23:51:59.259000+00:00
Status: Ready
Health: Green
Later, to deploy latest changes, commit them and run eb deploy <environment_name> or just eb deploy.
You are ready
That’s all! Run eb open to open your app in the browser.
Next Steps
Complete your configuration with the Ecosystem File.
Monitor your app on a web dashboard, with PM2 Plus.